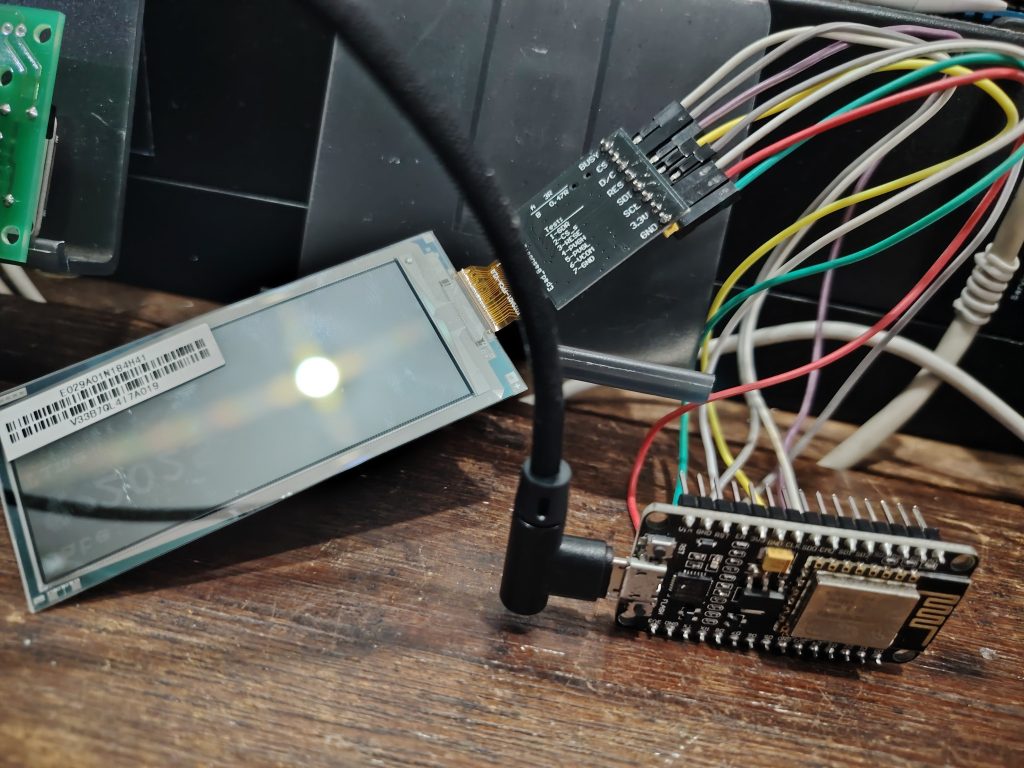
ตั้งแต่ยุคโบราณไดโนเสาร์พึ่งถือกำเนิดเกิดมา การจะเรียนรู้อุปกรณ์อะไรสักอย่าง ต้องรู้จริง ตั้งใจจริง เรียนรู้วงจร และเขียนโปรแกรมอย่างละเอียด เช่นสมัยก่อน จะเรียนรู้แค่สั่งงานจอ LCD แบบสองบรรทัด ต้องอ่านหนังสือเป็นเล่ม ฮาร์ดแวร์ต้องแม่น เขียนโปรแกรมต้องเฉียบคม ยากจริง!! ทำให้การเรียนรู้ถูกจำกัดเฉพาะนักอิเล็กทรอนิกส์เท่านั้น!!
แต่ยุคปัจจุบัน เทคโนโลยีเปลี่ยนเร็ว ทุกอย่างมีให้พร้อม เราสามารถเห็นความสำเร็จก่อนเริ่มต้นด้วยซ้ำ อยากสั่งงานพัดลมแบบ ioT วงจรก็มา หาซื้อง่าย ราคาถูก อยากเขียนโปรแกรมกับอุปกรณ์ ก็ไปหาไลบารี่มาใช้ให้ถูก ชีวิตช่างสุขสบาย เป็นโลกกว้างของนัก diy ไม่ต้องจบอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ เป็นงูเป็นปลา ขอแค่ขยันหน่อย มีทริกเล็กน้อย ก็สามารถเรียนรู้ได้ ทำโปรเจคที่สะเทือนวงการได้ไม่ยาก
epaper ซื้อมา ยังไม่รู้ว่าคืออะไรเลย หาข้อมูลทาง google ดูคลิปทาง youtube ก็อปตัดแปะจากลิงค์ คอมพาย ทำงานได้ซะงั้น ![]()
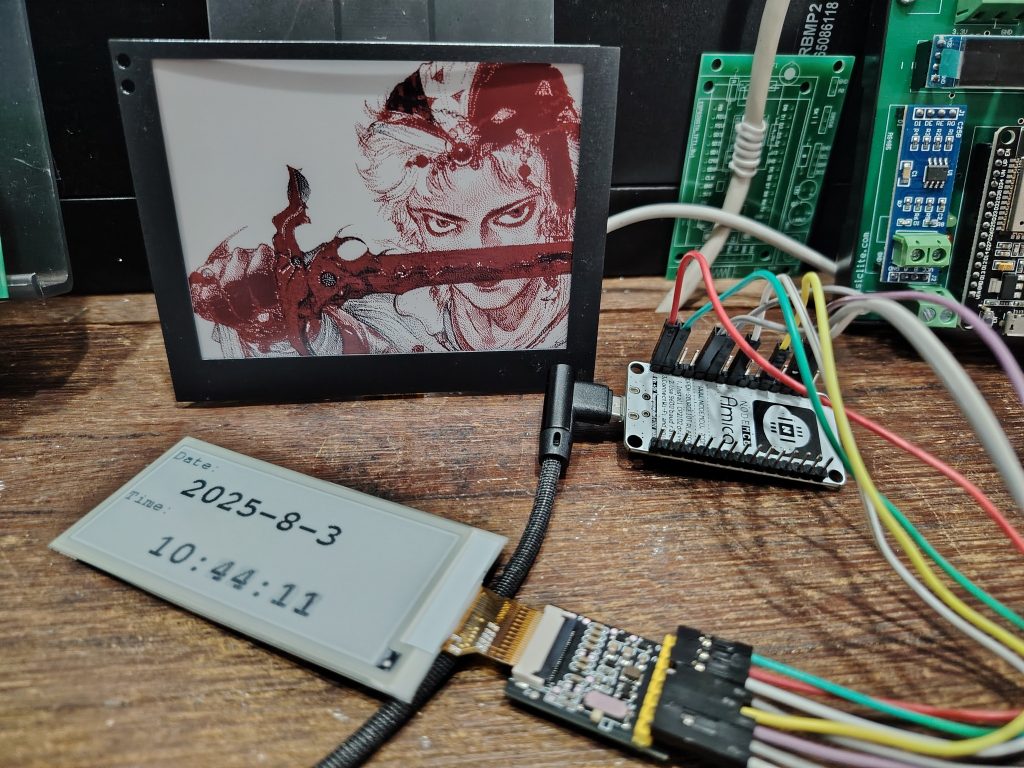
epaper คืออะไร เป็นเทคโนโลยีที่ถูกพัฒนาเรียนแบบการลงหมึกบนกระดาษจริงๆ และมีความสามารถเปลี่ยนเนื้อหาการแสดงผลด้วยระบบอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ ไม่ต้องใช้แสง Backlight ใช้พลังงานต่ำ สั่งแสดงผลเสร็จดึงไฟออก อักษรหรือภาพที่แสดงจะติดค้าง(โดยไม่ต้องใช้พลังงานไฟฟ้าเลย) หน้าจอแบบ epaper ซื้อมาทดสอบ แบบ 2 สี(ขาว ,ดำ) ขนาด 2.9 นิ้ว และแบบ 3 สี(ขาว ,ดำ ,แดง) ขนาด 4.2 นิ้ว ควบคุมสั่งงานใช้ ESP8266 ครับผม ส่วนโปรแกรมก็ไปก็อปของชาวบ้านมาเลย ง่ายสุดๆ
ขา cs = 15 ,reset = 2 ,dc = 4 ,busy = 5 ,sdi = 13 ,scl = 14
// base class GxEPD2_GFX can be used to pass references or pointers to the display instance as parameter, uses ~1.2k more code
// enable or disable GxEPD2_GFX base class
#define ENABLE_GxEPD2_GFX 0
#include <GxEPD2_BW.h>
#include <GxEPD2_3C.h>
#include <Fonts/FreeMonoBold9pt7b.h>
#include <Fonts/FreeMonoBold18pt7b.h>
#include <TimeLib.h>
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <WiFiUdp.h>
// ESP8266 CS(SS)=15,SCL(SCK)=14,SDA(MOSI)=13,BUSY=16,RES(RST)=5,DC=4
// 2.13” EPD Module
GxEPD2_BW<GxEPD2_290, GxEPD2_290::HEIGHT> display(GxEPD2_290(/*CS=D8*/ 15, /*DC=D3*/ 4, /*RST=D4*/ 2, /*BUSY=D2*/ 5)); // GDEH029A1 128×296, SSD1608 (IL3820)
//GxEPD2_3C<GxEPD2_213_Z98c, GxEPD2_213_Z98c::HEIGHT> display(GxEPD2_213_Z98c(/*CS=5*/ 15, /*DC=*/ 4, /*RES=*/ 2, /*BUSY=*/ 16)); // GDEY0213Z98 122×250, SSD1680
const char ssid[] = “****”; // your network SSID (name)
const char pass[] = “****”; // your network password
String formatted_date = “2000-01-01”;
String formatted_time = “00:00:00”;
// NTP Servers:
static const char ntpServerName[] = “us.pool.ntp.org“;
const int timeZone = 7; // Central European Time
WiFiUDP Udp;
unsigned int localPort = 8888; // local port to listen for UDP packets
time_t getNtpTime();
void sendNTPpacket(IPAddress &address);
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) ; // Needed for Leonardo only
delay(250);
Serial.println(“TimeNTP Example”);
Serial.print(“Connecting to “);
Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.begin(ssid, pass);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(“.”);
}
Serial.print(“IP number assigned by DHCP is “);
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
Serial.println(“Starting UDP”);
Udp.begin(localPort);
Serial.print(“Local port: “);
Serial.println(Udp.localPort());
Serial.println(“waiting for sync”);
setSyncProvider(getNtpTime);
setSyncInterval(300);
display.init(115200, false, 50, false);
header_text();
delay(1000);
refreshing_white();
delay(1000);
}
time_t prevDisplay = 0; // when the digital clock was displayed
void header_text()
{
formatted_date = String(year()) + “-” + String(month()) + “-” + String(day());
int16_t tbx, tby;
uint16_t tbw, tbh;
display.getTextBounds(formatted_date, 0, 0, &tbx, &tby, &tbw, &tbh);
uint16_t x = ((display.width() – tbw) / 2) – tbx;
display.setRotation(1);
display.setFont(&FreeMonoBold9pt7b);
display.setTextColor(GxEPD_BLACK);
display.setFullWindow();
display.firstPage();
do
{
display.fillScreen(GxEPD_WHITE);
display.setCursor(0, 15);
display.print(“Date:”);
display.setCursor(0, 75);
display.print(“Time:”);
display.setFont(&FreeMonoBold18pt7b);
display.setCursor(x, 50);
display.print(formatted_date);
}
while (display.nextPage());
}
void refreshing_white()
{
// Box for time and date
uint16_t box_w = 200;
uint16_t box_h = 30;
// calculate the center position
uint16_t box_x = (display.width() – box_w) / 2;
uint16_t box_y = ((display.height() – box_h) / 2) + 40;
for (uint16_t r = 1; r < 15; r++)
{
display.setRotation(1);
display.setPartialWindow(box_x, box_y, box_w, box_h);
display.firstPage();
do
{
display.fillRect(box_x, box_y, box_w, box_h, GxEPD_WHITE);
}
while (display.nextPage());
delay(200);
}
}
void showPartialUpdate()
{
//delay(100);
// Box for time and date
uint16_t box_w = 200;
uint16_t box_h = 30;
// calculate the center position
uint16_t box_x = (display.width() – box_w) / 2;
uint16_t box_y = ((display.height() – box_h) / 2) + 40;
uint16_t incr = display.epd2.hasFastPartialUpdate ? 1 : 3;
display.setFont(&FreeMonoBold18pt7b);
if (display.epd2.WIDTH < 104) display.setFont(0);
display.setTextColor(GxEPD_BLACK);
display.setRotation(1);
display.setPartialWindow(box_x, box_y, box_w, box_h);
display.firstPage();
do
{
display.fillRect(box_x, box_y, box_w, box_h, GxEPD_WHITE);
int16_t tbx, tby;
uint16_t tbw, tbh;
display.getTextBounds(formatted_time, 0, 0, &tbx, &tby, &tbw, &tbh);
// Hitung posisi tengah kotak
int16_t x = box_x + (box_w – tbw) / 2;
int16_t y = box_y + (box_h – tbh) / 2 + tbh;
display.setCursor(x, y);
display.print(formatted_time);
}
while (display.nextPage());
}
void loop() {
formatted_time = String(hour() < 10 ? “0” : “”) + String(hour()) + “:” +
String(minute() < 10 ? “0” : “”) + String(minute()) + “:” +
String(second() < 10 ? “0” : “”) + String(second());
showPartialUpdate();
//delay(10000);
if (formatted_date != String(year()) + “-” + String(month()) + “-” + String(day())) {
header_text();
delay(1000);
refreshing_white();
delay(1000);
}
}
/*——– NTP code ———-*/
const int NTP_PACKET_SIZE = 48; // NTP time is in the first 48 bytes of message
byte packetBuffer[NTP_PACKET_SIZE]; //buffer to hold incoming & outgoing packets
time_t getNtpTime()
{
IPAddress ntpServerIP; // NTP server’s ip address
while (Udp.parsePacket() > 0) ; // discard any previously received packets
Serial.println(“Transmit NTP Request”);
// get a random server from the pool
WiFi.hostByName(ntpServerName, ntpServerIP);
Serial.print(ntpServerName);
Serial.print(“: “);
Serial.println(ntpServerIP);
sendNTPpacket(ntpServerIP);
uint32_t beginWait = millis();
while (millis() – beginWait < 1500) {
int size = Udp.parsePacket();
if (size >= NTP_PACKET_SIZE) {
Serial.println(“Receive NTP Response”);
Udp.read(packetBuffer, NTP_PACKET_SIZE); // read packet into the buffer
unsigned long secsSince1900;
// convert four bytes starting at location 40 to a long integer
secsSince1900 = (unsigned long)packetBuffer[40] << 24;
secsSince1900 |= (unsigned long)packetBuffer[41] << 16;
secsSince1900 |= (unsigned long)packetBuffer[42] << 8;
secsSince1900 |= (unsigned long)packetBuffer[43];
return secsSince1900 – 2208988800UL + timeZone * SECS_PER_HOUR;
}
}
Serial.println(“No NTP Response ![]() “);
“);
return 0; // return 0 if unable to get the time
}
// send an NTP request to the time server at the given address
void sendNTPpacket(IPAddress &address)
{
// set all bytes in the buffer to 0
memset(packetBuffer, 0, NTP_PACKET_SIZE);
// Initialize values needed to form NTP request
// (see URL above for details on the packets)
packetBuffer[0] = 0b11100011; // LI, Version, Mode
packetBuffer[1] = 0; // Stratum, or type of clock
packetBuffer[2] = 6; // Polling Interval
packetBuffer[3] = 0xEC; // Peer Clock Precision
// 8 bytes of zero for Root Delay & Root Dispersion
packetBuffer[12] = 49;
packetBuffer[13] = 0x4E;
packetBuffer[14] = 49;
packetBuffer[15] = 52;
// all NTP fields have been given values, now
// you can send a packet requesting a timestamp:
Udp.beginPacket(address, 123); //NTP requests are to port 123
Udp.write(packetBuffer, NTP_PACKET_SIZE);
Udp.endPacket();
}
//**********************************